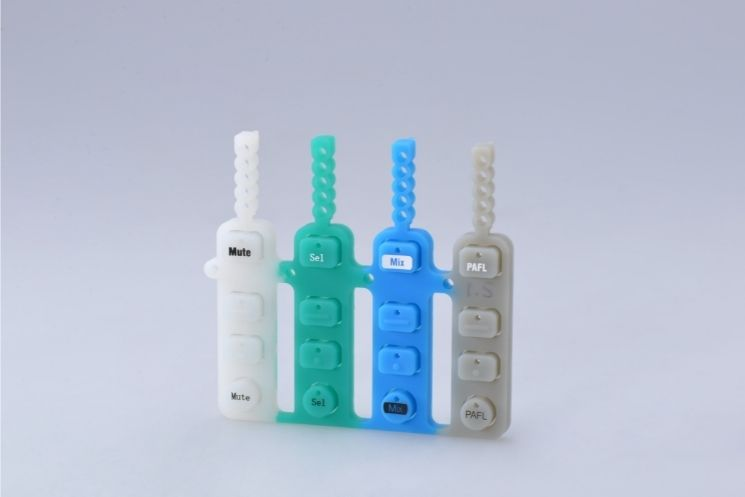
An Overview
Vacuum Casting is a process in which a liquid material is drawn into a silicone mold whilst using a vacuum, to create complex components. The liquid materials used for vacuum casting are elastomers such as plastic and rubber.
Vacuum casting is sometimes referred to as polyurethane casting or urethane casting as polyurethane resin, a type of elastomer, is used as the casting material. Vacuum casting is an economical alternative to injection molding for making plastic components as the production cost of vacuum casting is comparatively lower.
Vacuum casting is an excellent production process for batch production and other low-volume production jobs. In India, Vacuum casting is heavily used in the FMCG and consumer product manufacturing as well as industrial electronics production.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. HOW DOES VACUUM CASTING WORK
· 3D Model of the component
· Creating master pattern of the mold
· Making silicone molds
· Casting polyurethane resin
· Curing and de-molding
2. USES OF VACUUM CASTING
· Commercial products manufacturing
· Food and beverages industry
· Electronic industry
3. BENEFITS OF VACUUM CASTING
4. DRAWBACKS OF VACUUM CASTING
5. BOTTOM LINE
HOW DOES VACUUM CASTING WORK?
Vacuum casting is very similar to injection molding, where the cast material is injected into molds for creating products. The difference between vacuum casting and injection molding is in the types of molds used.
In injection molding, molds are made of aluminum, steel, etc. On the other hand in vacuum casting, silicone molds are used. This greatly reduces the cost of mold making, as silicone is cheaper and it also possesses good durability.
The casting material most commonly used in this process is polyurethane. Different polyurethanes have different properties, such as good structural rigidity, elasticity, flexibility, shock and temperature resistance and so on. Thus depending on the type of product being manufactured, different polyurethanes can be used.
The vacuum casting process can be broken down into the following 5 steps:
1. 3D MODEL OF THE COMPONENT
The first step in making any vacuum cast component is creating a 3D model of the required component. The model is made using the same design guidelines used for making molds in injection molding.
Proper calculations must be made before creating the 3D model. Deformities in the model can affect the final product after casting. Hence it is important to follow design guidelines properly and make proper adjustments to the calculations wherever required.

2. CREATING MASTER PATTERN OF THE MOLD
The master pattern of the mold is made using 3D rendering. This pattern is the primary mold that is used for making the silicone molds which will then be used for casting. It is a prototype that is used for making silicone molds, and it is made from high durability materials such as metals or other plastics.
Earlier master patterns were made using CNC or hand tools, but these days processes such as 3D printing, stereolithography, and various others are used, to make it more economical, with greater precision techniques.
As the silicone molds are copies of the master pattern, any deformation on the pattern itself will result in the deformation of the silicone molds. Hence, a high degree of precision is required while preparing the master pattern.
3. MAKING SILICONE MOLDS
After making the master pattern, the next step is to make silicone molds. Silicone molds are made directly using the master pattern and a casting box.
The master pattern is suspended inside the casting box. Cores and inserts are fitted on the inside of the master pattern. Along with the core, casting gates and risers are also placed in the casing box for pouring the molten silicone and removing the final mold respectively.
Hot, molten silicone is poured into the casting box, around the master pattern. It flows inside the master pattern, filling all the crevices of the prototype mold. The molten silicone is allowed to cure inside the casting box, which is maintained at 40*C, for about 8-16 hours.
After the silicone has solidified and the curing is completed, risers are removed and the silicone mold is taken out of the casting box. The whole process is completed under vacuum, to maintain casting deformations to a minimum.
4. PREPARING POLYURETHANE RESIN
Before casting, the polyurethane (PU) resin mixture is prepared by mixing the resin and other casting components, such as pigments and other agents, and heating the resin. Depending upon the type of product to be manufactured, different types of polyurethanes are available, with different material and structural qualities.
The resin mixture is made by combining the two parts of the resin in a container and heating the mixture at about 40*C . Color pigments are also mixed at this stage. Before pouring the resin mixture into the molds, it should be noted that the resin and the pigments have completely mixed into a homogeneous solution.
After the solution is complete, it is poured into the silicone molds using a funnel for uniform distribution and to prevent any formation of air bubbles. Once the solution has been poured completely, the mold is sealed and it is ready for casting.
5. CURING AND DEMOLDING
After the solution is completely set in the mold and the mold is properly sealed, it is placed in the vacuum casting machine for casting.
Depending on the type of polyurethane used, the temperature and time for casting may vary, but the process remains the same. After the casting is complete, the mold is left in the casting machine for curing. Curing helps the cast retain its structural rigidity after it is removed from the mold.
The casting machine is maintained at around 70°C to properly cure the cast. After the curing is complete, the mold is taken out of the machine and its two halves separated to properly remove the cast. It is important to de-mold the cast properly, ensure the cast is not damaged while being removed from the mold. Excess materials such as the gates and runners are trimmed off while removing the cast from the mold.
Thus the casting of the resin is complete and the product is ready to be used.
USES OF VACUUM CASTING
Vacuum casting is a highly economical and efficient alternative to the traditional injection molding process for making complex and intricate products.
Vacuum casting is used extensively in the commercial products manufacturing industry, because of the efficient nature of production.
Some of the industries where vacuum casting is used are:
1. CONSUMER PRODUCTS MANUFACTURING
Consumer products such as sunglasses, pens, and other stationery products, cosmetic packages, combs and hair brushes are made more efficiently using vacuum casting.
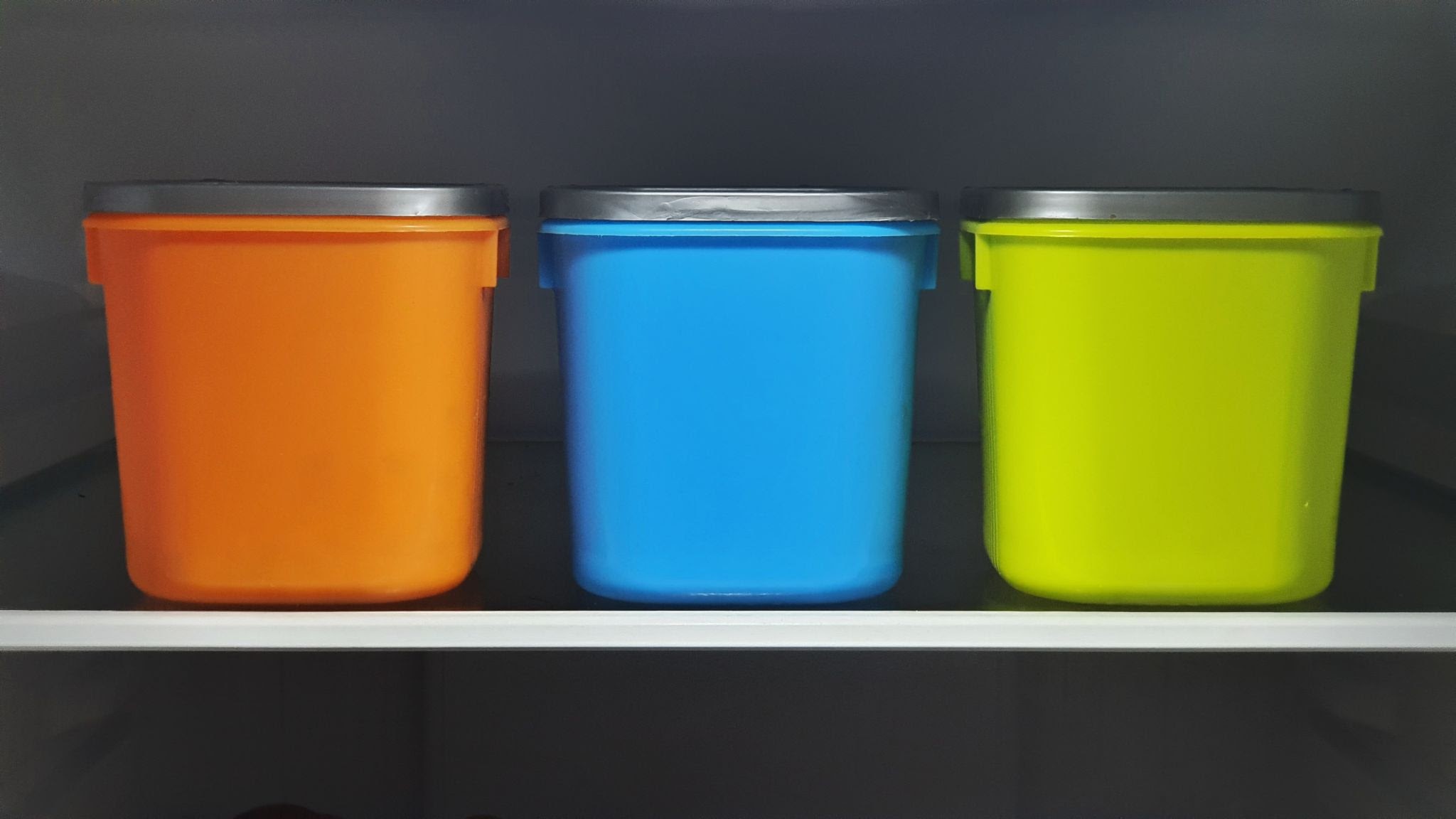
2. FOOD AND BEVERAGES INDUSTRY
Food and beverages packaging, food containers, bottles, cans, mugs, and glasses are made using vacuum casting.
As rapid manufacturing is a key aspect in these industries, vacuum casting is extensively used due to the quick manufacturing nature and high efficiency of the process.


3. ELECTRONIC INDUSTRIES
Polyurethanes have excellent shock and heat resistance. Thus vacuum casting using polyurethanes is a preferred manufacturing process for making housings of electronic devices.

BENEFITS OF VACUUM CASTING
Vacuum casting is a highly efficient manufacturing process. Intricate and delicate shapes can be manufactured easily, with high precision, and at a lower cost.
Some of the advantages of using vacuum casting for manufacturing are:
· Complex and intricate shapes can be easily manufactured with high precision.
· Multiple components can be simultaneously manufactured, increasing the efficiency of production.
· Rapid prototyping using high-quality urethane is possible for small batch production.
· Different polyurethanes have different material properties. Hence a variety of products can be manufactured using different polyurethanes.
· Material cost of polyurethane is low, hence manufacturing is highly economical.
· Silicone molds are easier to manufacture than metal molds. Hence mold manufacturing can be efficiently done.
DRAWBACKS OF VACUUM CASTING
Although vacuum casting is a very efficient manufacturing process, like every other manufacturing process it also has a few drawbacks.
· In vacuum casting the molds are made of silicone and compared to injection molding, where the molds are made of metal, the lifespan of silicone is very less. Hence wearing of molds is very common.
· Apart from mold wearing, the mold size in vacuum casting is also limited to about 40-50 molds. Hence vacuum casting is more suitable for low-volume production than mass production.
· Regular cleaning of molds is very important in vacuum casting, as residue from the previous cast will lead to off-marks on the subsequent cast.
· Silicone molds are subjected to shrinkage due to thermal expansion. The shrinkage rate of commercial silicone is from 1% to 4%. Hence, it is important to use high-quality silicone, with a lower shrinkage rate for mold making in vacuum casting.
· Although the production cost of vacuum casting is very low, the initial cost of setup may be high, depending upon the tools, equipment, etc.
COMPETENCIES OF KARKHANA.IO
Vacuum casting is a highly economical and efficient manufacturing process. The manufacturing costs in vacuum casting are more economical as compared to traditional methods such as plastic injection molding and pressure die casting.
The economical nature of manufacturing makes vacuum casting highly efficient for batch production jobs and rapid prototyping jobs, where limited amounts of products are to be manufactured.
Vacuum casting is not as efficient for mass production as other traditional manufacturing processes, as only a limited number of products can be cast at a single time.
Thus for small-quantity batch production and rapid prototyping, vacuum casting is a great manufacturing process, with efficient manufacturing and economical production.
It is a versatile and highly adaptive manufacturing process. Hence, it is the preferred production process for custom and low volume manufacturing jobs.
If you wish to get Vacuum casting expertise in your city for your manufacturing needs, look no further! Karkhana.io serves client orders of all sizes from small batches to large volumes.
Let us help you reach the optimal outcome for all your manufacturing requirements.To get started, simply email Alay Shah on alay@karkhana.io with your requirements or fill out the form below.
Sign up and connect with us!