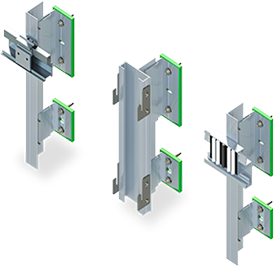
Fabrication Stainless Steel
Material Description
Stainless steel is a highly versatile and widely used engineering material known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. It is primarily composed of iron, with at least 10.5% chromium content, which forms a protective passive oxide layer on the surface, preventing rust and corrosion. This alloy can also contain other elements like nickel, molybdenum, and titanium, further enhancing its durability and performance characteristics.
Stainless steel is categorized into several grades, each tailored to specific applications, offering a wide range of properties such as high-temperature resistance, exceptional strength, and superior hygienic qualities. Its durability and resistance to various environmental factors make it ideal for a diverse array of applications, including construction, automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and kitchenware. Additionally, its lustrous appearance and easy maintenance have contributed to its popularity in architectural and decorative applications. The unique combination of mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal makes stainless steel a key material in numerous technical and industrial settings.
Grades
304, 316, 430
Finishing Options
Passivation, Electropolishing, Passivation, Bead Blasting, Grinding, Polishing, PVD Coating, Powder Coating, Painting
| Density | Tensile Yield Strength (MPa) | Fatigue Strength (MPa) | Hardness (Brinell) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m-K) | Coeff. of Thermal Expansion (mm/mdeg) | Electrical Resistivity (micro Ohm-cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8000 | 200-700 | 200-500 | 150 - 320 | ~16-25 | 16 | 70-80 |
Design Recommendation
When designing with stainless steel, it’s essential to prioritize material selection, as stainless steel offers remarkable durability, corrosion resistance, and a sleek aesthetic. Opt for the appropriate grade of stainless steel based on the intended application, considering factors like exposure to moisture, temperature variations, and potential chemical exposure. Additionally, maintain a clean and consistent design language to accentuate the material’s modern, timeless appeal. Incorporate rounded edges and smooth surfaces for both aesthetics and ease of maintenance. Finally, remember that stainless steel can be recycled, so embracing sustainability by designing for disassembly and recyclability is a responsible choice for environmentally conscious projects.
Cost Saving Tip
Stainless steel is known for its high abrasiveness, so selecting the right cutting tools is crucial. Carbide or ceramic tools designed for stainless steel are ideal. Effective coolant flow is essential to dissipate heat and reduce tool wear, leading to cost savings by prolonging tool life.